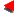
Indian Muntjac,Barking Deer
(Muntiacus muntjak)
Habitat: forests and bushes in low altitude mountains and hills.
Feeding habits: nibble
at vegetation with its mouth. Food:
branches, leaves, flowers and fruits of vegetation and crops.
Size: with a body length of 1 m and a tail length of 17-21 cm; weight: 25-30 kg. Habits: Barking deer usually acts alone. It is cautious and sensitive. It often comes out in the night, in early morning, or at dusk. During daytime, it usually hides in bushes to take rests. They will bark when they are frightened and their bark is quite similar with that of dogs. Barking deer have fixed range of action. No matter how far away they are chased from a place, they will always return to their original dwelling place. Barking deer has good production ability and they can mate all the year round. Its pregnant period is about 210 days and can produce 1 baby each time. Barking deer's sex is matured at the age of one year. Its skin is an important leather making raw material and it is one of the main animals of hunting in South China.
Category: mammalia, artiodactyls, deer.
Distribution: all over Yunnan, Southeast, South and Southwest China.
Level of protection: it's not listed in the name list of animals being protected.

|